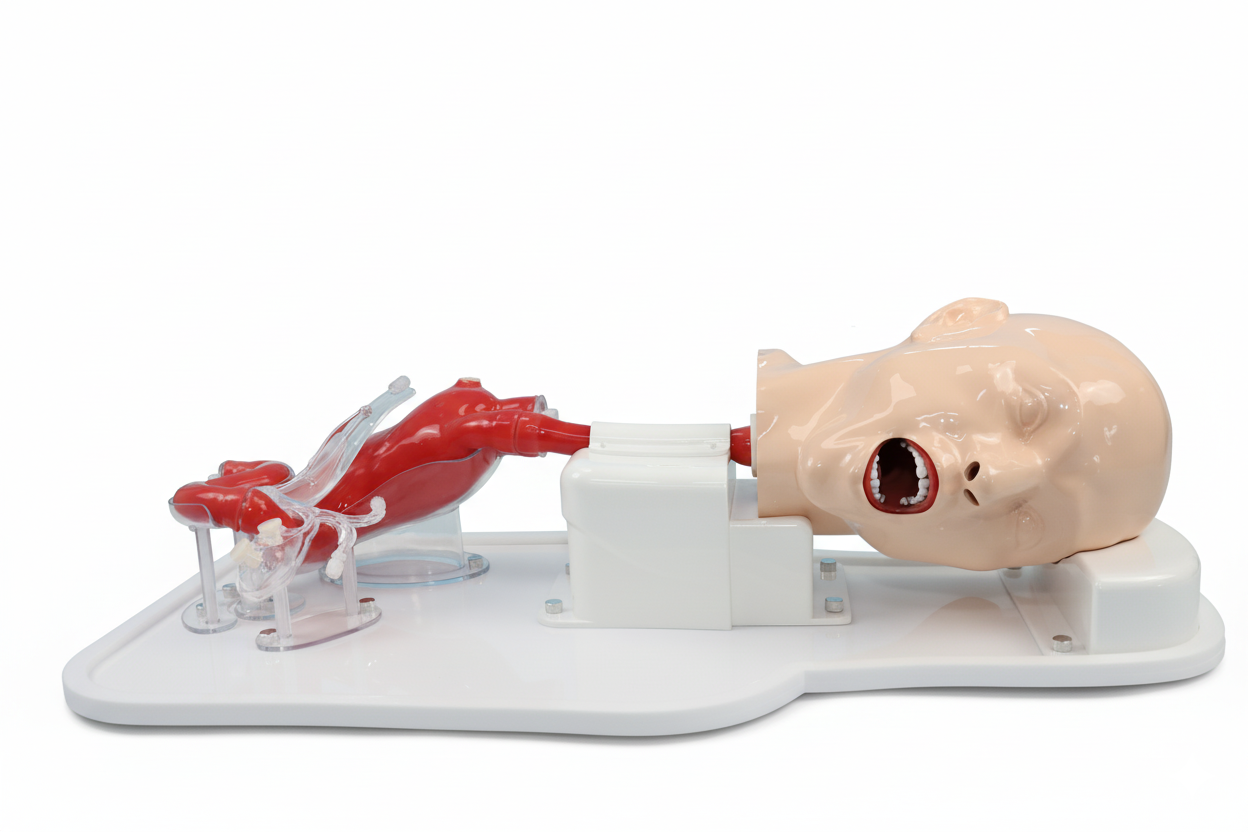
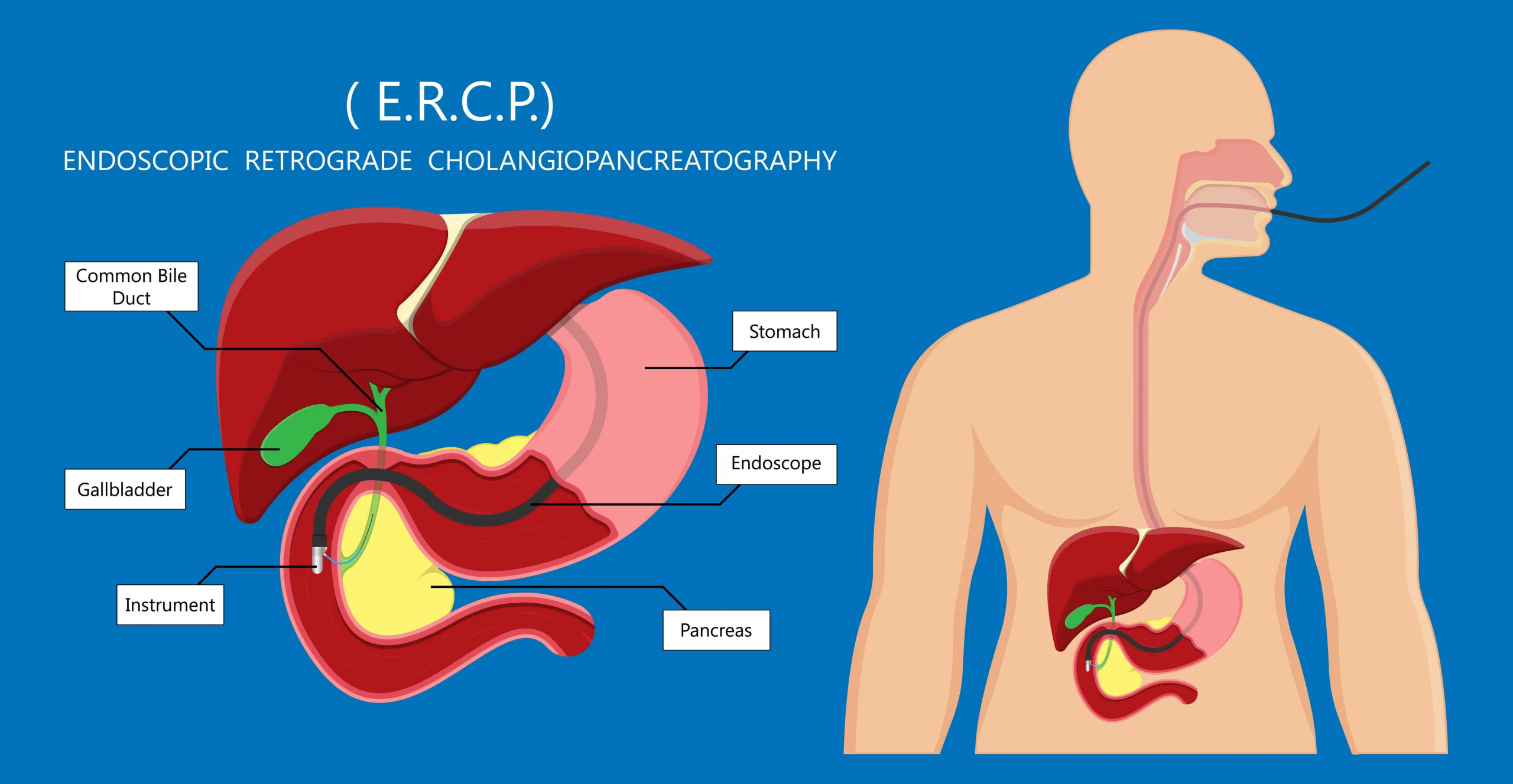
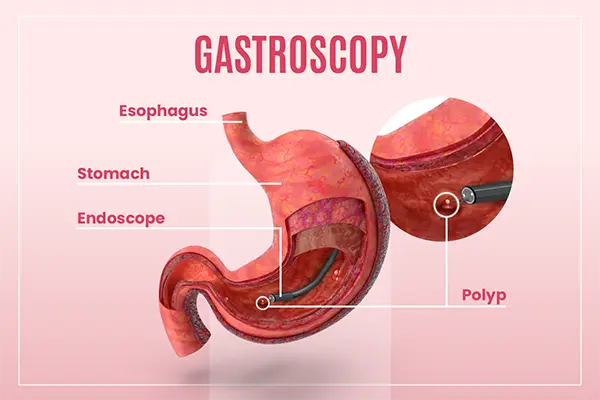
With the advancement of digestive endoscopy, gastroscopy and ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) are now widely applied not only for diagnosis but also for therapeutic interventions. However, clinical training carries risks and limitations, especially for beginners. High-fidelity medical simulation models have therefore become an essential tool in endoscopic education.
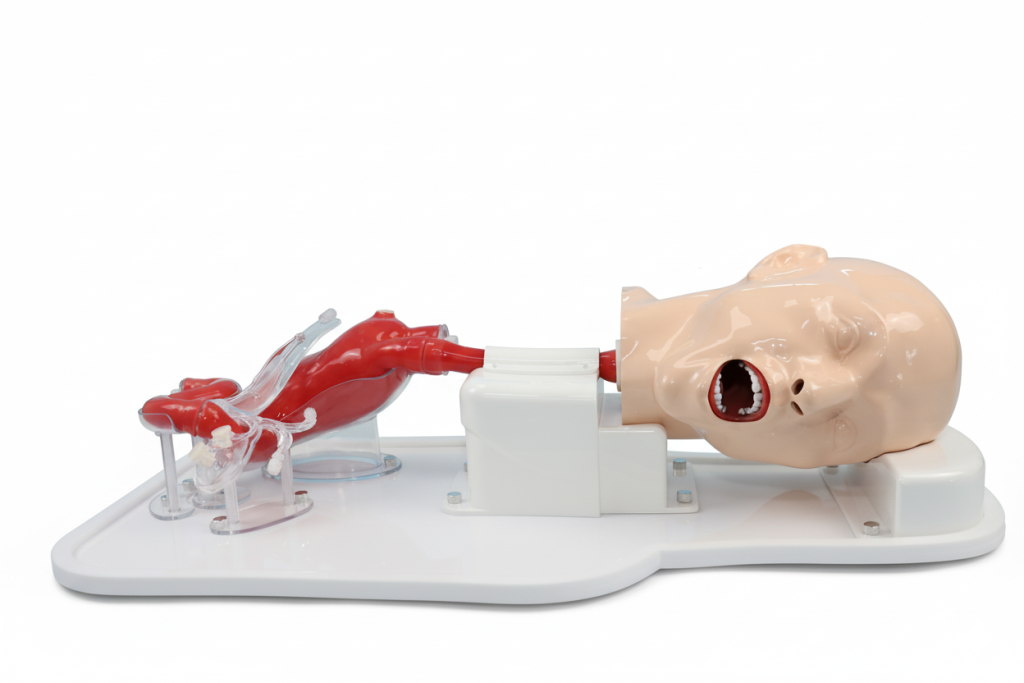
Advantages of Simulation
Safety: Practicing gastroscopy or ERCP on real patients involves risks such as bleeding or pancreatitis. Simulators provide a risk-free environment for repeated training. Repetition & Flexibility: Models allow endless practice of bile duct cannulation, papilla access, stone extraction, and stent placement. Anatomy or difficulty can be adjusted to match training needs. Skill Development: Endoscopy requires strong hand–eye coordination. Simulators help learners build spatial awareness and muscle memory in different patient positions, accelerating adaptation to clinical practice. Teaching & Assessment: Beyond practice, simulators support structured evaluation. Instructors can observe procedures, provide feedback, and use scoring systems to measure progress.
Applications
Gastroscopy Trainer: Trainees can explore the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, while learning to identify ulcers, polyps, or bleeding sites. ERCP Trainer: Simulation enables safe training of cannulation, stone removal, and stent deployment in prone or semi-prone positions. Integrated Pathway: Combining gastroscopy and ERCP models creates a complete training route from basic to advanced skills.
Medical simulation models are not only training tools but also a cornerstone of modern medical education. By offering safe, repeatable, and standardized practice, simulators reduce risk, improve confidence, and shorten the learning curve—ultimately enhancing the success and safety of advanced endoscopic procedures.