Gastroscopy and ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) are both commonly performed procedures in digestive endoscopy. While they may appear similar, they differ in examination range, patient positioning, procedural complexity, and clinical purpose.
Gastroscopy: The Foundation
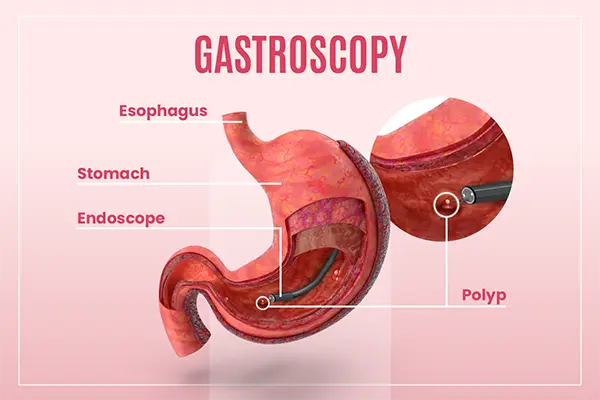
Gastroscopy examines the esophagus, stomach, and duodenal bulb.
- Indications: gastritis, ulcers, bleeding, tumor screening.
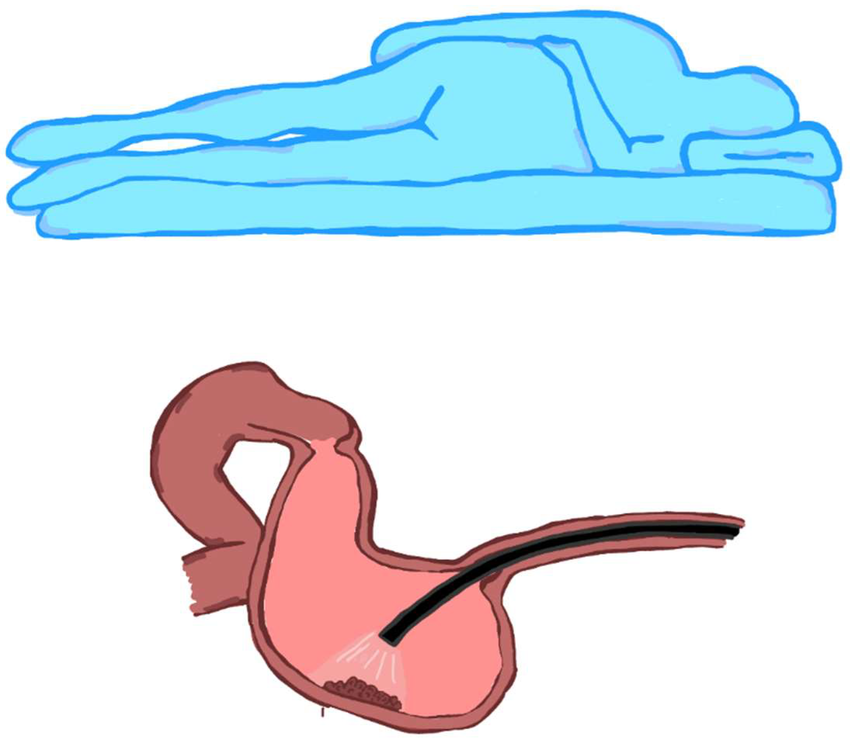
- Patient positioning: left lateral decubitus to reduce aspiration risk and facilitate secretion drainage.
- Clinical use: primarily diagnostic, with some therapeutic procedures such as biopsy, polypectomy, and hemostasis.
- Learning curve: relatively easy; considered an essential entry-level skill for all endoscopists.
ERCP: Advanced Therapeutic Procedure
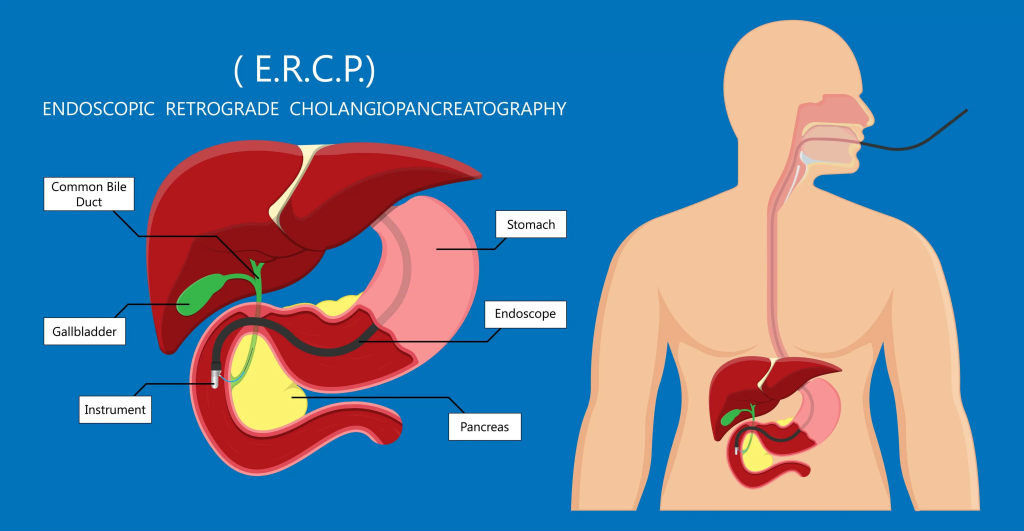
ERCP extends the examination to the descending duodenum and requires cannulation of the bile and pancreatic ducts.
- Indications: common bile duct stones, biliary obstruction, strictures, pancreatic diseases.
- Patient positioning: prone or semi-prone to better expose the duodenal papilla.
- Clinical use: mainly therapeutic (stone extraction, dilation, sphincterotomy, stent placement).
- Learning curve: high; requires precise endoscope control and strong spatial awareness.
Role of Endoscopic Models
Simulation models allow safe, repeatable practice:
- Gastroscopy: insertion techniques, anatomy recognition, pylorus navigation.
- ERCP: duodenal navigation, papilla localization, duct cannulation, stone extraction, stent placement.
Using these models accelerates skill acquisition and shortens the learning curve while maintaining patient safety.
您好,这是一条评论。若需要审核、编辑或删除评论,请访问仪表盘的评论界面。评论者头像来自 Gravatar。